jdk线程池的分为两类:ExecutorService和ScheduledExecutorService
jdk对应的实现类为ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor组成 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 new ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maxinumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler); //corePoolSize --核心线程数,线程池中创建的线程数小于核心线程数时,线程空闲也不会被回收;大于核心线程数时,线程空闲时间超过keepAliveTime个unit单位,线程就会被回收 //maxinumPoolSize --最大线程数,线程池中所能创建的最大的线程个数,超过将执行handler里面的拒绝策略. //keepAliveTime --线程最大空闲时间,作用在上面已说明 //unit --时间单位,作用在上面已说明 //workQueue --工作队列,超过核心线程数时,任务会放在工作队列中.工作队列满了,才会再创建最大线程内的线程. //threadFactory --线程工厂,实现创建线程的接口(有默认实现:Executors.defaultThreadFactory()) //handler --拒绝策略,实现拒绝任务的接口(有默认实现: defaultHandler)
三种工厂方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 ExecutorService fixedPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(8 );ExecutorService cachedPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();ExecutorService singlePool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ExecutorService的主要方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 execute(Runnable task); Future<T> submit (Runnable task) ; Future<T> submit (Callable<T> task) ; List<Future<T>> invokeAll (List<Callable<T>> taskList) ; List<Future<T>> invokeAll (List<Callable<T>> taskList, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) ; T invokeAny (ListCallable<T> taskList) ; T invokeAny (ListCallable<T> taskList, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) ; shutdown();
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 package per.guc.gucproject.test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.concurrent.*;public class ThreadPool { public static void main (String[] args) { ExecutorService fixedPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(8 ); ExecutorService cachedPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); ExecutorService singlePool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Runnable runTask = new Runnable () { @Override public void run () { System.out.println("run..." ); } }; fixedPool.execute(runTask); Future<?> submit = fixedPool.submit(runTask); Callable callTask = new Callable <Object>() { @Override public Object call () throws Exception { System.out.println("call..." ); return "1" ; } }; Future submit1 = fixedPool.submit(callTask); List<Callable<Object>> callableList = new ArrayList <>(); try { List<Future<Object>> futures = fixedPool.invokeAll(callableList); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } try { List<Future<Object>> futures = fixedPool.invokeAll(callableList, 1000 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } try { Object o = fixedPool.invokeAny(callableList); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } try { Object o1 = fixedPool.invokeAny(callableList, 1000 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (TimeoutException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } fixedPool.shutdown(); try { Object result = submit.get(); System.out.println(result); Object result1 = submit1.get(); System.out.println(result1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } }
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor组成 1 2 3 4 public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor (int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) ;
四种工厂方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ##重要 ScheduledExecutorService和ExecutorService主要区别在于阻塞队列不同,ScheduledExecutorService内部是用DelayedWorkQueue的实现队列 ScheduledExecutorService ses1 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(8 );ScheduledExecutorService ses2 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(8 , Executors.defaultThreadFactory());ScheduledExecutorService ses3 = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();ScheduledExecutorService ses4 = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
ScheduledExecutorService 主要方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit); ScheduledFuture<T> schedule (Callable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) ; ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit); ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit);
示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 package per.guc.gucproject.test;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Slf4j public class ScheduledExecutorTest { public static void main (String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); scheduledExecutorService.schedule(()->{ log.debug("rate task..." ); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }, 1000 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); scheduledExecutorService.schedule(()->{ log.debug("rate task..." ); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }, 1000 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{ log.debug("rate task..." ); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }, 1000 , 1000 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(()->{ log.debug("delay task..." ); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }, 1000 , 1000 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } }
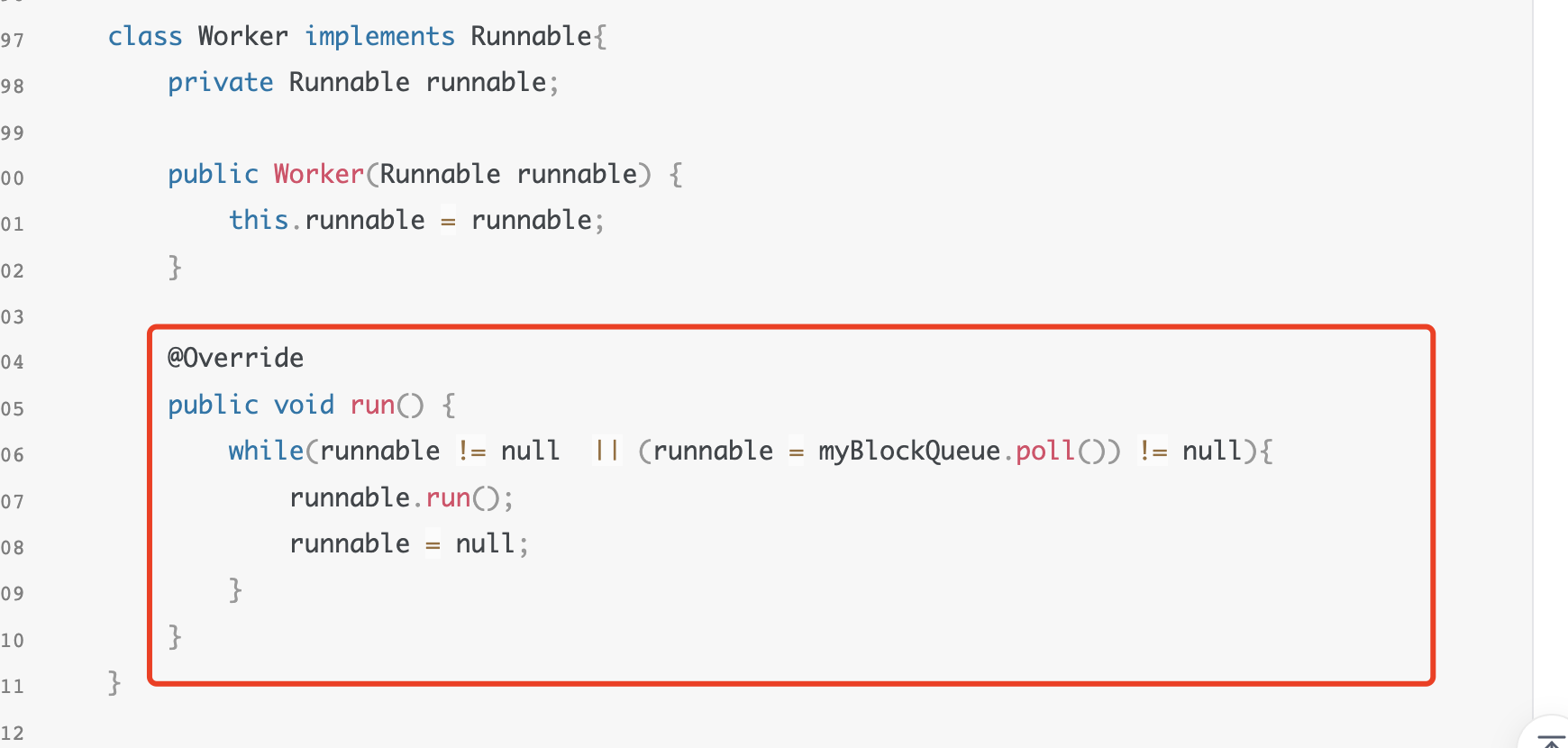
手写线程池代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 package per.guc.gucproject.test; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; @Slf4j public class MyThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThreadPool myThreadPool = new MyThreadPool(2, 2); myThreadPool.execute(()->{ log.debug("task1 run..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } log.debug("task1 finished..."); }); myThreadPool.execute(()->{ log.debug("task2 run..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } log.debug("task2 finished..."); }); myThreadPool.execute(()->{ log.debug("task3 run..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } log.debug("task3 finished..."); }); myThreadPool.execute(()->{ log.debug("task4 run..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } log.debug("task4 finished..."); }); myThreadPool.execute(()->{ log.debug("task5 run..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } log.debug("task5 finished..."); }); } } class MyThreadPool{ //coreThreadSize private int coreSize; //blockQueue; private MyBlockQueue myBlockQueue; //计数器 private AtomicInteger atomicInteger; public MyThreadPool(int coreSize, int blockQueueSize) { this.coreSize = coreSize; this.myBlockQueue = new MyBlockQueue(blockQueueSize); this.atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1); } public void execute(Runnable runnable){ int threadSize = atomicInteger.get(); if(threadSize > coreSize){ myBlockQueue.put(runnable); return; } if(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(threadSize, threadSize+1)) { int threadName = threadSize; Worker worker = new Worker(runnable); Thread thread = new Thread(worker, "t"+ threadName); thread.start(); } } class Worker implements Runnable{ private Runnable runnable; public Worker(Runnable runnable) { this.runnable = runnable; } @Override public void run() { while(runnable != null || (runnable = myBlockQueue.poll()) != null){ runnable.run(); runnable = null; } } } } @Slf4j class MyBlockQueue{ //队列容量 int capacity; BlockingDeque<Runnable> linkedQueue; public MyBlockQueue(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; this.linkedQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(); this.lock = new ReentrantLock(); this.emptyWait = lock.newCondition(); this.fullWait = lock.newCondition(); } Lock lock; Condition emptyWait; Condition fullWait; public Runnable poll(){ lock.lock(); try{ if(linkedQueue.size() == 0){ try { log.debug("任务获取进入阻塞等待"); emptyWait.await(); log.debug("任务获取被唤醒"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } log.debug("获取到队列头任务"); Runnable task = linkedQueue.removeFirst(); fullWait.signalAll(); return task; }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void put(Runnable task){ lock.lock(); try{ if(linkedQueue.size() == capacity){ try { log.debug("任务存放进入阻塞等待"); fullWait.await(); log.debug("任务存放被唤醒"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } log.debug("存放到队列尾任务"); linkedQueue.addLast(task); emptyWait.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
代码分析 核心代码分析,新建worker任务类,重写run方法,第一个任务是对象构建的时候传入的任务,后面的任务是从阻塞队列取出的.如果阻塞队列没有任务了,线程会阻塞在阻塞队列获取任务的await方法上.
延迟线程池使用的队列是DelayedWorkQueue,内部属性queue采用的是RunnableScheduledFuture[]数组,该接口继承的是Delayed接口.
可以采用DelayQueue来实现任务的延迟执行,内部实现了PriorityQueue,一个优先级队列.放入的任务需要实现Delay接口的,内部会根据任务的优先级进行排序.
参考博客: https://biteeniu.github.io/java/java-delay-queue/