二分算法
条件:数组或者列表对象事先都要经过排序.
思路:
数组:
1.先对数组进行最大值下标和最小值下标的初始化
2.循环判断最大值是否大于等于最小值
2.1 取最大值和最小值的中间下标.
2.2目标值去对比中间下标的取值
2.3如果相等则返回中间值下标对应的数组值退出
2.4如果下标值比目标值大,则将中间值下标减一赋值给最大值下标,然后跳转到步骤2
2.5如果下标值比目标值小,则将中间值下标加一赋值给最小值下标,然后跳转到步骤2
3.退出循环时返回null.
链表:
1.判断链表节点是否为空
1.1取节点的数据和目标数据相比
1.2如果相等则返回节点对象对应的数据退出
1.3如果取出的节点数据比目标数据大,则将当前节点赋值为当前节点的右节点,然后跳转到步骤1
1.4如果取出的节点数据比目标数据小,则将当前节点赋值为当前节点的左节点,然后跳转到步骤1
2.退出循环时返回null.
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Binary {
public <T extends Comparable> T algorithm(T[] array, T target){
int min = 0;
int max = array.length-1;
while(max >= min){
int mid = (max+min)/2;
if(target.compareTo(array[mid])==0){
return array[mid];
}else if(target.compareTo(array[mid])<0){
max = mid-1;
}else{
min = mid+1;
}
}
return null;
}
public <T extends Comparable> T algorithmLinked(Node<T> node, T target){
while(node != null) {
if (target.compareTo(node.getData()) == 0) {
return node.getData();
}else if(target.compareTo(node.getData()) == -1){
node = node.getLeft();
}else{
node = node.getRight();
}
}
return null;
}
class Node<T> {
private T data;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(Node left) {
this.left = left;
}
public Node getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(Node right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
}
|
分治算法:
场景:汉诺塔游戏用例
思路:
1.如果只有1个圆盘,那就是从a移动到c结束
2.num>=2,分治思想:把圆盘看成两部分,第num个和第num-1组
2.1.先到把num-1组从a移动到b,中间会借助c
2.2然后再把num个组a移动到c
2.3最后再把num-1组从b移动到c,中间会借助a
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Partition {
public int count = 0;
public void move(char a, char b, char c,int num){
count++;
if(num == 1){
System.out.println("第"+num+"个圆盘,从"+a+"移动到"+c);
}else{
move(a, c, b, num-1);
System.out.println("第"+num+"个圆盘,从"+a+"移动到"+c);
move(b, a, c, num-1);
}
}
}
|
该算法的优缺点:
缺点:时间复杂度为2^n,效率是低下的.优点:采用分治算法,步骤非常好理解且代码量很低,比较好实现
动态规划算法
场景:01背包存放物品展现背包最大价值.
思路:
需要构建一个横坐标为背包容量,纵坐标为商品编号的二维数组.
1.商品编号为1的商品,如果商品容量大于背包容量,则为0;如果商品容量小于等于背包容量,则背包最大价值等于商品1的价值
2.继续增加编号为2的商品,如果当前背包容量小于当前2号商品的容量,则等于编号为1时的背包容量的最大价值;如果当前背包容量大于等于2号商品的容量,则需要判断(2号商品的价值+背包存放当前编号数量和背包容量减去2号商品容量的最大价值)去和之前最大价值比较取最大值,如图:

如下面示例的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
for(int i=1; i< knapsackVal.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < knapsackVal[i].length; j++) {
if(itemCapacity[i-1] > j) {
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j];
}else{
if(knapsackVal[i-1][j]>knapsackVal[i-1][j-itemCapacity[i-1]]+itemValue[i-1]){
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j];
}else{
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j-itemCapacity[i-1]]+itemValue[i-1];
knapsackItem[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
|
完整代码如下,其中代码还包括最大价值背包当中存放的有哪些编号的商品,数组knapsackItem[][]描述,值为1时表示当前坐标下它被放入背包,如图:
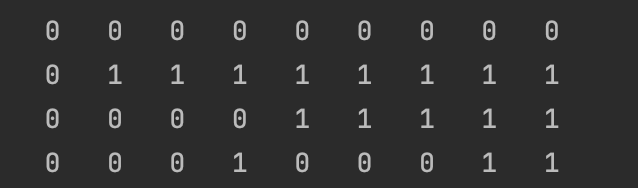
整体示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Dynamic {
public int knapsackCal(int knapsackCapacity, int[] itemCapacity, int[] itemValue){
int[][] knapsackVal = new int[itemCapacity.length+1][knapsackCapacity+1];
int[][] knapsackItem = new int[itemCapacity.length+1][knapsackCapacity+1];
for(int i=0; i<knapsackVal.length; i++){
knapsackVal[i][0] = 0;
}
for(int j=0; j<knapsackVal[0].length; j++){
knapsackVal[0][j] = 0;
}
for(int i=1; i< knapsackVal.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < knapsackVal[i].length; j++) {
if(itemCapacity[i-1] > j) {
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j];
}else{
if(knapsackVal[i-1][j]>knapsackVal[i-1][j-itemCapacity[i-1]]+itemValue[i-1]){
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j];
}else{
knapsackVal[i][j] = knapsackVal[i-1][j-itemCapacity[i-1]]+itemValue[i-1];
knapsackItem[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<knapsackVal.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < knapsackVal[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%4d", knapsackVal[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
for(int i=0; i<knapsackItem.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < knapsackItem[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%4d", knapsackItem[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
int i = knapsackItem.length-1;
int j = knapsackItem[0].length-1;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if(knapsackItem[i][j]==1){
System.out.println("第"+i+"编号商品放入背包");
j -= itemCapacity[i-1];
}
i--;
}
return knapsackVal[itemCapacity.length][knapsackCapacity];
}
}
|
KMP算法(暴力破解算法的优化)
场景:解决字符串匹配的问题
思路:
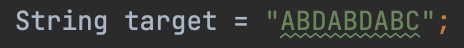
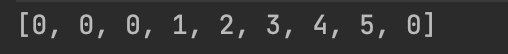
将需要匹配的目标字符串构建部分匹配表,初始下标的值默认为-1,如下图:
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int[] targetLength =new int[target.length()];
for(int i=1, j=0; i<targetLength.length; i++){
if(target.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)){
j++;
}else{
j=0;
}
targetLength[i] = j;
}
|
1构建好匹配表后,原字符串和目标字符串都从开始下标位置开始匹配.
1.1 如果相等
1.1.1则将原字符串和目标字符串的下标都对应加1.
1.1.2同时去判断目标数组的下标是否等于目标字符串的长度了.
1.1.2.1如果相等,则返回原字符串的下标减去目标字符串的长度就为对应原匹配字符串的起始下标位置
1.1.2.2如果不相等,则返回到步骤1
1.2如果不相等
1.2.1则去判断目标数组的下标是否为0
1.2.1.1如果为0,则将原数组的下标加1
1.2.2将目标数组的下标赋值为部分匹配数组的值,然后返回到步骤1
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
int indexSource = 0;
int targetSource = 0;
while(indexSource<source.length()){
if(source.charAt(indexSource) != target.charAt(targetSource)){
if(targetSource == 0){
indexSource++;
}
targetSource = targetLength[targetSource];
}else{
indexSource++;
targetSource++;
if(targetSource == target.length()){
return indexSource -targetSource;
}
}
}
|
此算法的特点时原字符的下标匹配的时候永远不会回退,时间复杂度为O{n}
完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Kmp {
public int findTargetStringIndex(String source, String target){
int[] targetLength =new int[target.length()];
for(int i=1, j=0; i<targetLength.length; i++){
if(target.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)){
j++;
}else{
j=0;
}
targetLength[i] = j;
}
int indexSource = 0;
int targetSource = 0;
while(indexSource<source.length()){
if(source.charAt(indexSource) != target.charAt(targetSource)){
if(targetSource == 0){
indexSource++;
}
targetSource = targetLength[targetSource];
}else{
indexSource++;
targetSource++;
if(targetSource == target.length()){
return indexSource -targetSource;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|
贪心算法
场景: 选择电台覆盖所有城市地区的问题
思路:
将所有电台所能覆盖的城市都汇聚成一个citySet集合,
//贪心算法的思路,每步中选出覆盖最多城市的电台
循环遍历每个电台所覆盖的城市是否在citySet集合中,统计每个电台的城市数量,并找出最大数量的电台.
将这个电台加入挑选出的电台集合中并移除这个电台在citySet集合中的城市并清除原有遍历的Map集合中的这个电台.
直到citySet为空时停止循环遍历
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Greedy {
public List<String> radioGreedy(Map<String, List<String>> allRadioMap){
Set<String> citySet = new HashSet<>();
allRadioMap.values().stream().collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(ll->citySet.addAll(ll));
List<String> radioList = new ArrayList<>();
while(!citySet.isEmpty()){
String maxCityKey = "";
int maxCityNum = 0;
for(Map.Entry<String,List<String>> entry: allRadioMap.entrySet()){
int keyCityNum = 0;
for(String city: entry.getValue()){
if(citySet.contains(city)){
keyCityNum++;
}
}
if(keyCityNum > maxCityNum){
maxCityNum = keyCityNum;
maxCityKey = entry.getKey();
}
}
radioList.add(maxCityKey);
citySet.removeAll(allRadioMap.get(maxCityKey));
allRadioMap.remove(maxCityKey);
}
return radioList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,List<String>> allRadioMap = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<String> k1 = new ArrayList<>();
k1.add("北京");
k1.add("石家庄");
k1.add("郑州");
ArrayList<String> k2 = new ArrayList<>();
k2.add("北京");
k2.add("上海");
k2.add("广州");
ArrayList<String> k3 = new ArrayList<>();
k3.add("南京");
k3.add("苏州");
k3.add("杭州");
k3.add("上海");
ArrayList<String> k4 = new ArrayList<>();
k4.add("南宁");
k4.add("南昌");
k4.add("成都");
ArrayList<String> k5 = new ArrayList<>();
k5.add("重庆");
k5.add("桂林");
k5.add("成都");
ArrayList<String> k6 = new ArrayList<>();
k6.add("广州");
k6.add("南京");
k6.add("成都");
allRadioMap.put("K1",k1);
allRadioMap.put("K2",k2);
allRadioMap.put("K3",k3);
allRadioMap.put("K4",k4);
allRadioMap.put("K5",k5);
allRadioMap.put("K6",k6);
Greedy greedy = new Greedy();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(greedy.radioGreedy(allRadioMap).toArray()));
}
}
|
普里姆算法
场景: 图平面求各个点之间连通的最短路径的问题
思路:
1.从1个顶点开始,求出这个顶点到其他各个顶点权值最小的路径.
2.把这个权值最小路径的顶点加入到已访问的顶点集合中,然后遍历这两个顶点到其他所有各个顶点权值最小的路径.
3.当然这个权值最小的路径的顶点不能是已加入访问顶点的路径
4.依次循环需要执行顶点总个数减一次,找到的边即为各个顶点的最短路径
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Prim {
public int shortWeight(char[] vertex, int[][] weight){
int[] visited = new int[vertex.length];
int sumWeight = 0;
for(int m=1,n=0; m<visited.length;m++) {
visited[n] = 1;
int minIndex = -1;
int visitedIndex = -1;
int minWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int j=0; j<visited.length&&visited[j]==1;j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < weight[j].length; i++) {
if (weight[j][i] < minWeight && visited[i] != 1) {
minWeight = weight[j][i];
minIndex = i;
visitedIndex = j;
}
}
}
System.out.println("边<"+vertex[visitedIndex]+vertex[minIndex]+">,权值为:"+minWeight);
sumWeight = sumWeight + minWeight;
n = minIndex;
}
return sumWeight;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertex = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G'};
int[][] weight = {{10000,3,6,8,4,1000,1},
{3,10000,10,5,19,8,4},
{6,10,10000,36,7,13,22},
{8,5,36,10000,9,12,33},
{4,19,7,12,10000,23,14},
{1000,8,13,12,23,10000,17},
{1,4,22,33,14,17,10000}};
Prim prim = new Prim();
System.out.println(prim.shortWeight(vertex, weight));
}
}
|
克鲁斯卡尔算法
场景: 和普里姆算法要解决的问题相同,也是各个顶点连通求最短路径
思路:
1.先把各个顶点所连通的边加入到边的集合中,然后把这个集合从小到大排序
2.排序完成之后,依次遍历,需要加入边不能形成回路(通过终点不能相同去判定)
3.找出顶点个数减一条边后即可求的各个顶点联通的最短路径.
算法核心代码,顶点的终点是否一致判断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
while(endVertex[tempEndVertex] != 0){
tempEndVertex = endVertex[tempEndVertex];
}
if(tempEndVertex != sides[i].endVertex){
if(tempEndVertex<sides[i].endVertex) {
endVertex[tempEndVertex] = sides[i].endVertex;
}else{
endVertex[sides[i].endVertex] = tempEndVertex;
}
}
|
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Kruskal {
public int shortWeight(char[] vertex, int[][] weight){
List<Side> sideList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<weight.length; i++){
for(int j=i+1; j<weight[i].length; j++){
sideList.add(new Side(i, j, weight[i][j]));
}
}
Side[] sides = sideList.toArray(new Side[sideList.size()]);
Arrays.sort(sides);
int[] endVertex = new int[vertex.length];
int sumWeight = 0;
for(int i=0; i<sides.length; i++){
int tempEndVertex = sides[i].startVertex;
while(endVertex[tempEndVertex] != 0){
tempEndVertex = endVertex[tempEndVertex];
}
if(tempEndVertex != sides[i].endVertex){
if(tempEndVertex<sides[i].endVertex) {
endVertex[tempEndVertex] = sides[i].endVertex;
}else{
endVertex[sides[i].endVertex] = tempEndVertex;
}
System.out.println("边<"+vertex[sides[i].startVertex]+vertex[sides[i].endVertex]+">,权值为:"+sides[i].weight);
sumWeight = sumWeight + sides[i].weight;
}
}
return sumWeight;
}
class Side implements Comparable<Side>{
int startVertex;
int endVertex;
int weight;
public Side(int startVertex, int endVertex, int weight) {
this.startVertex = startVertex;
this.endVertex = endVertex;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Side s) {
if(weight<s.weight){
return -1;
}else if(weight > s.weight){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertex = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G'};
int[][] weight = {{10000,3,6,8,4,1000,1},
{3,10000,10,5,19,8,4},
{6,10,10000,36,7,13,22},
{8,5,36,10000,9,12,33},
{4,19,7,12,10000,23,14},
{1000,8,13,12,23,10000,17},
{1,4,22,33,14,17,10000}};
Kruskal kruskal = new Kruskal();
System.out.println(kruskal.shortWeight(vertex, weight));
}
}
|
执行结果和普里姆算法的结果一致
迪杰斯特拉算法
场景: 解决目标顶点到各顶点的最短路径
思路:
1.创建一个目标顶点的权值数组,初始化赋值为边与边不通的值
2.创建一个可以被访问顶点的数组
3.初始化count默认为顶点数
4.遍历目标顶点的边的权值,如果小于目标顶点的权值,则赋值为边的权值,并将该下标对应的可以被访问的顶点设置为1,并将count-1
5.循环遍历已被设置被访问顶点,如果目标顶点到被访问顶点的距离加上被访问顶点到遍历点的距离小于目标顶点到遍历点的距离,则将该值替换为目标顶点到遍历点的距离,并将count-1.
6.每次循环遍历结束时,去统计count是否小于等于0,如果小于等于了,则再遍历顶点个数次
7.遍历结束后输出的目标顶点的权值数组就为目标顶点到各顶点的最小权值路径.
代码如下,验证代码结果是正确的(和佛洛依德算法一致),但代码逻辑应该还是可以有优化的地方.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Dijkstra {
public void vertexShortWeight(char[] vertex, int[][] weight, int index){
int[] targetWeight = new int[vertex.length];
for(int i=0; i< targetWeight.length; i++){
targetWeight[i] = 10000;
}
int[] vertexReady = new int[vertex.length];
int count = vertex.length;
for(int i=0; i<weight[index].length; i++){
if(weight[index][i]<targetWeight[i]){
targetWeight[i] = weight[index][i];
vertexReady[i] = 1;
count--;
}
}
int indexStart = 0;
int endWhile =vertex.length;
boolean flag = true;
while(flag||endWhile>0){
endWhile--;
if(vertexReady[indexStart] ==1){
for(int j=0; j<weight[indexStart].length; j++){
if((weight[indexStart][j]+targetWeight[indexStart])<targetWeight[j]){
targetWeight[j] = weight[indexStart][j] + targetWeight[indexStart];
vertexReady[j] = 1;
count--;
}
}
}
indexStart = (indexStart+1)%vertex.length;
if(flag&&count<=0){
flag = false;
endWhile = vertex.length;
}
}
System.out.println("顶点"+vertex[index]);
for(int i=0; i<vertex.length; i++){
System.out.print("到"+vertex[i]+"的距离("+targetWeight[i]+")");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertex = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G'};
int[][] weight = {{0,7,10000,10000,10000,2,6},
{7,0,6,10000,10000,10000,10},
{10000,6,0,4,10000,10000,8},
{10000,10000,4,0,9,10000,8},
{10000,10000,10000,9,0,3,10000},
{2,10000,10000,10000,3,0,10000},
{6,10,10000,8,10000,10000,0}};
Dijkstra dijkstra = new Dijkstra();
dijkstra.vertexShortWeight(vertex, weight, 3);
}
}
|
佛洛依德算法
场景: 解决目标顶点到各顶点的最短路径
思路:
1.利用中间节点遍历起始顶点到各个终止顶点的距离
2.如果相比小于起始顶点到终止顶点的距离,则将其是顶点到终止顶点的距离值赋值为利用中间节点的距离
3.如果相比大于起始顶点到终止顶点的距离,则保持不变
优点: 思路代码很好实现,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
public class Floyd {
public void vertexShortWeight(char[] vertex, int[][] weight, int index){
for(int k=0; k<vertex.length; k++){
for(int i=0; i< vertex.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j< vertex.length; j++){
int len = weight[i][k] + weight[k][j];
if(len < weight[i][j]){
weight[i][j] = len;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("顶点"+vertex[index]);
for(int i=0; i<vertex.length; i++){
System.out.print("到"+vertex[i]+"的距离("+weight[index][i]+")");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertex = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G'};
int[][] weight = {{0,3,6,8,4,1000,1},
{3,0,10,5,19,8,4},
{6,10,0,36,7,13,22},
{8,5,36,0,9,12,33},
{4,19,7,12,0,23,14},
{1000,8,13,12,23,0,17},
{1,4,22,33,14,17,0}};
Floyd floyd = new Floyd();
floyd.vertexShortWeight(vertex, weight, 0);
}
}
|
马塔回旋算法
通过递归回溯的算法实现的:
1.先创建一个棋盘的二维数组,创建对应每个点是否已被访问的数组,是否完成的标识
2.创建一个对象,用数值表示横纵坐标的属性值
3.创建一个方法,得到下一步的所有刚才对象的集合,利用棋盘的边界大小去判断
4.写出马踏棋盘的算法的方法,有当前棋盘的行和列和步骤,初始为1.
6.将行和列赋值给对应的二维数组的坐标,值为初始步骤,并将对应已访问的数组的对应值设为已访问
5.创建当前对象,初始化行和列的值,调用下一步的方法.
6.判断得到的集合是否为空,不为空则调用集合的remove(0)方法删除并得到删除的对象,如果对象没有被访问过,则递归调用刚才马踏棋盘的方法.如果已被调用,则继续对集合判断是否为空,重复第六步的操作.
7.退出while循环后,需要判断step是否小于棋盘的格子数并且是未完成,如果满足,则需要将当前对象的行列对应的二维数组置为0,并且访问数组对应的下标设置成位访问.如果不满足,则将是否完成设置为已完成.
优化点,先让马走贴近棋盘边缘的步骤,因为这样得到下一步的组合比较少,计算耗时会比较少
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
| package per.xiaotian.datasort.algorithm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class HorseChessboard {
private int[][] chessBoard;
private boolean[] visited;
private boolean finished;
public static void main(String[] args) {
HorseChessboard horseChessboard = new HorseChessboard();
int len =6;
horseChessboard.chessBoard = new int[len][len];
horseChessboard.visited = new boolean[len*len];
System.out.println("======start=======");
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
horseChessboard.cal(4, 4, 1);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()-curTime);
System.out.println("======end=======");
for(int i=0;i<horseChessboard.chessBoard.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<horseChessboard.chessBoard[i].length; j++){
System.out.printf("%4d", horseChessboard.chessBoard[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void cal(int x, int y, int step){
chessBoard[x][y] = step;
visited[chessBoard.length*x+y] = true;
ChessBoard cur = new ChessBoard();
cur.x = x;
cur.y = y;
List<ChessBoard> chessBoardList = next(cur);
Collections.sort(chessBoardList);
while(!chessBoardList.isEmpty()){
ChessBoard next = chessBoardList.remove(0);
if(!visited[chessBoard.length*next.x+next.y]){
cal(next.x, next.y, step+1);
}
}
if(step<chessBoard.length*chessBoard[0].length&&!finished){
chessBoard[x][y] = 0;
visited[chessBoard.length*x+y] = false;
}else{
finished = true;
}
}
public List<ChessBoard> next(ChessBoard cur){
List<ChessBoard> chessBoardList = new ArrayList<>();
if(cur.x -2>=0 && cur.y-1>=0){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x-2;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y-1;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x -2>=0 && cur.y+1<chessBoard[0].length){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x-2;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y+1;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x -1>=0 && cur.y+2<chessBoard[0].length){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x-1;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y+2;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x -1>=0 && cur.y-2>=0){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x-1;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y-2;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x +2<chessBoard.length && cur.y-1>=0){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x+2;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y-1;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x +2<chessBoard.length && cur.y+1<chessBoard[0].length){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x+2;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y+1;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x +1<chessBoard.length && cur.y+2<chessBoard[0].length){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x+1;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y+2;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
if(cur.x +1<chessBoard.length && cur.y-2>=0){
ChessBoard chessBoard1 = new ChessBoard();
chessBoard1.x = cur.x+1;
chessBoard1.y = cur.y-2;
chessBoardList.add(chessBoard1);
}
return chessBoardList;
}
class ChessBoard implements Comparable<ChessBoard>{
int x;
int y;
@Override
public int compareTo(ChessBoard o) {
int size1 = next(o).size();
int size2 = next(this).size();
return size2-size1;
}
}
}
|




